| LTPDA Toolbox™ | contents |   |
The LTPDA method ao/tfe estimates the transfer function of time-series
signals, included in the input aos following the Welch's averaged, modified periodogram method [1].
Data are windowed prior to the estimation of the spectra, by multiplying
it with a spectral window object, and can be detrended by polinomial of time in order to reduce the impact
of the border discontinuities. The window length is adjustable to shorter lenghts to reduce the spectral
density uncertainties, and the percentage of subsequent window overlap can be adjusted as well.
b = tfe(a1,a2,pl)
a1 and a2 are the 2 aos containing the input time series to be evaluated, b is the output object and pl is an optional parameters list.
As an alternative to setting the number of points 'Nfft' in each window, it's possible to ask for a given number of TFE estimates by setting the 'Navs' parameter, and the algorithm takes care of calculating the correct window length, according to the amount of overlap between subsequent segments.
| If the user doesn't specify the value of a given parameter, the default value is used. |
The function makes transfer functions estimates between the 2 input aos, and the output will contain the transfer function estimate from the first ao to the second.
The algorithm is based in standard MATLAB's tools, as the ones used by pwelch. The standard deviation of the mean is computed as
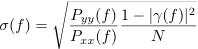
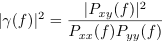
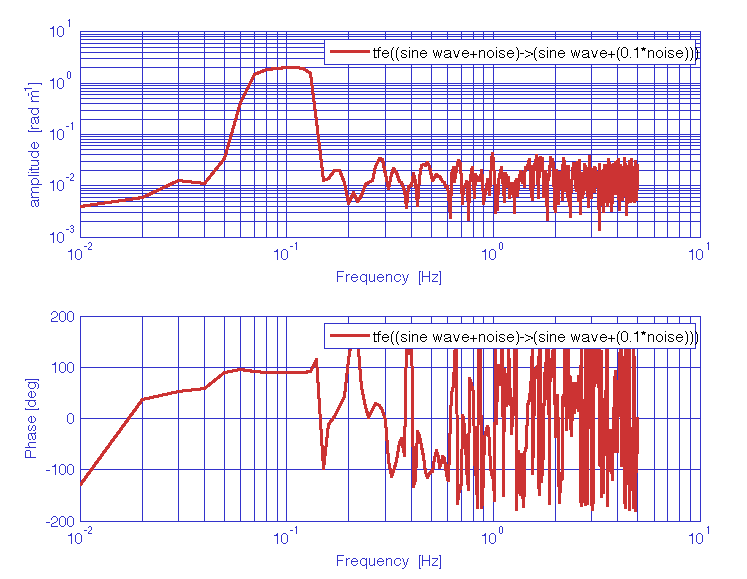
Evaluation of the transfer function between two time-series represented by: a low frequency sinewave signal superimposed to white noise, and a low frequency sinewave signal at the same frequency, phase shifted and with different amplitude, superimposed to white noise.
% parameters
nsecs = 1000;
fs = 10;
% create first signal AO
x = ao(plist('waveform','sine wave','f',0.1,'A',1,'nsecs',nsecs,'fs',fs)) + ...
ao(plist('waveform','noise','type','normal','nsecs',nsecs,'fs',fs));
x.setYunits('m');
% create second signal AO
y = ao(plist('waveform','sine wave','f',0.1,'A',2,'nsecs',nsecs,'fs',fs,'phi',90)) + ...
0.1*ao(plist('waveform','noise','type','normal','nsecs',nsecs,'fs',fs));
y.setYunits('rad');
% compute transfer function
nfft = 1000;
psll = 200;
Txy = tfe(x,y,plist('win','Kaiser','psll',psll,'nfft',nfft));
% plot
iplot(Txy)
 |
Cross coherence estimates | Log-scale power spectral density estimates |  |
©LTP Team